Difference between revisions of "Benign non-inflammatory skin conditions"
m (→Microscopic evaluation: packed) |
m (heights) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===Epidermis=== | ===Epidermis=== | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed> | + | <gallery mode=packed heights=190> |
File:Histopathology of chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis.jpg|'''Ulceration''': On the outer ear, consider chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis: With the ulceration surrounded by acanthosis and parakeratosis. | File:Histopathology of chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis.jpg|'''Ulceration''': On the outer ear, consider chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis: With the ulceration surrounded by acanthosis and parakeratosis. | ||
File:Micrograph of perinuclear vacuolization, annotated.jpg|'''Perinuclear vacuolization''', most likely insignificant as an isolated finding. In case of dermatitis, consider '''[[Vacuolar interface dermatitis]]''' | File:Micrograph of perinuclear vacuolization, annotated.jpg|'''Perinuclear vacuolization''', most likely insignificant as an isolated finding. In case of dermatitis, consider '''[[Vacuolar interface dermatitis]]''' | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===Dermis=== | ===Dermis=== | ||
====Sebaceous glands==== | ====Sebaceous glands==== | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed | + | <gallery mode=packed heights=190> |
File:Histopathology of sebaceous hyperplasia.jpg|Sebaceous hyperplasia: Multiple, mature sebaceous lobules attached to the central dilated duct in the upper dermis.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Sato|first1=Toshitsugu|last2=Tanaka|first2=Masaru|title=Linear sebaceous hyperplasia on the chest|journal=Dermatology Practical & Conceptual|year=2014|issn=21609381|doi=10.5826/dpc.0401a16}}</ref> | File:Histopathology of sebaceous hyperplasia.jpg|Sebaceous hyperplasia: Multiple, mature sebaceous lobules attached to the central dilated duct in the upper dermis.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Sato|first1=Toshitsugu|last2=Tanaka|first2=Masaru|title=Linear sebaceous hyperplasia on the chest|journal=Dermatology Practical & Conceptual|year=2014|issn=21609381|doi=10.5826/dpc.0401a16}}</ref> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
====Fatty tissue==== | ====Fatty tissue==== | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed | + | <gallery mode=packed heights=190> |
File:Histopathology of lipoma.jpg|[[Lipoma]]: The mass is composed of lobules of mature white adipose tissue divided by delicate and inconspicuous fibrous septa containing thin-walled capillary-sized vessels.<ref name="Kim2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kim|first1=Hei Sung |title=Lipoma on the antitragus of the ear|journal=Journal of Clinical Research in Dermatology|volume=3|issue=2|year=2016|pages=01–02|issn=23781726|doi=10.15226/2378-1726/3/2/00121}}</ref> | File:Histopathology of lipoma.jpg|[[Lipoma]]: The mass is composed of lobules of mature white adipose tissue divided by delicate and inconspicuous fibrous septa containing thin-walled capillary-sized vessels.<ref name="Kim2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kim|first1=Hei Sung |title=Lipoma on the antitragus of the ear|journal=Journal of Clinical Research in Dermatology|volume=3|issue=2|year=2016|pages=01–02|issn=23781726|doi=10.15226/2378-1726/3/2/00121}}</ref> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
===Elastosis=== | ===Elastosis=== | ||
'''[[Elastosis]]''' is the buildup of elastin in tissues. | '''[[Elastosis]]''' is the buildup of elastin in tissues. | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed | + | <gallery mode=packed heights=190> |
File:Micrograph of solar elastosis.jpg|Actinic (or "solar") elastosis. | File:Micrograph of solar elastosis.jpg|Actinic (or "solar") elastosis. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{{Bottom}} | {{Bottom}} | ||
Revision as of 10:08, 5 March 2020
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
These are aberrations that do not display signs of suspected malignant excisions or dermatitis:
Contents
Fixation
Generally 10% neutral buffered formalin.
See also: General notes on fixation
Gross processing
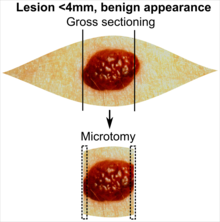
| <4 mm | 4 - 8 mm | 9 - 15 mm |
|---|---|---|
In table above, each top image shows recommended lines for cutting out slices to be submitted for further processing. Bottom image shows which side of the slice that should be put to microtomy. Dashed lines here mean that either side could be used. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions
Microscopic evaluation
The primary objective is to determine the location, and then the most likely cell type of the aberration:
Epidermis
Perinuclear vacuolization, most likely insignificant as an isolated finding. In case of dermatitis, consider Vacuolar interface dermatitis
Dermis
Sebaceous glands
Sebaceous hyperplasia: Multiple, mature sebaceous lobules attached to the central dilated duct in the upper dermis.[2]
Fatty tissue
Elastosis
Elastosis is the buildup of elastin in tissues.
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑
- . Handläggning av hudprover – provtagningsanvisningar, utskärningsprinciper och snittning (Handling of skin samples - sampling instructions, cutting principles and incision. Swedish Society of Pathology.
- For number of slices and coverage of lesions, as well as including sections from each edge in case of diffuse border. - . Dermatopathology Grossing Guidelines. University of California, Los Angeles. Retrieved on 2019-10-23.
- For microtomy of the most central side at the lesion - "The principles of mohs micrographic surgery for cutaneous neoplasia
- With a "standard histologic examination" that, in addition to the lesion, only includes one section from each side along the longest diameter of the specimen.
- It also shows an example of circular coverage, with equal coverage distance in all four directions.
- The entire specimen may be submitted if the risk of malignancy is high. - . Handläggning av hudprover – provtagningsanvisningar, utskärningsprinciper och snittning (Handling of skin samples - sampling instructions, cutting principles and incision. Swedish Society of Pathology.
- ↑ Sato, Toshitsugu; Tanaka, Masaru (2014). "Linear sebaceous hyperplasia on the chest ". Dermatology Practical & Conceptual. doi:. ISSN 21609381.
- ↑ Kim, Hei Sung (2016). "Lipoma on the antitragus of the ear ". Journal of Clinical Research in Dermatology 3 (2): 01–02. doi:. ISSN 23781726.
Image sources