Difference between revisions of "Breast biopsy or excision"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Microscopic evaluation: Introduced) |
(→Malignancy: Expanded) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
*Invasive cancer | *Invasive cancer | ||
| + | ===Most common types=== | ||
{|class="wikitable" align="center" | {|class="wikitable" align="center" | ||
|+ Women seeking evaluation of a breast lump<ref name="Kumar">{{cite book |author1=Mitchell, Richard Sheppard |author2=Kumar, Vinay |author3=Abbas, Abul K. |author4=Fausto, Nelson |title=Robbins Basic Pathology |edition=8th |publisher=Saunders |location=Philadelphia |year= 2007|page=739 |isbn=978-1-4160-2973-1 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> | |+ Women seeking evaluation of a breast lump<ref name="Kumar">{{cite book |author1=Mitchell, Richard Sheppard |author2=Kumar, Vinay |author3=Abbas, Abul K. |author4=Fausto, Nelson |title=Robbins Basic Pathology |edition=8th |publisher=Saunders |location=Philadelphia |year= 2007|page=739 |isbn=978-1-4160-2973-1 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Finding |
| − | ! | + | ! Relative<br> incidence |
| + | ! Histopathology | ||
| + | ! Image | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Fibrocystic breast changes || 40% | + | | Fibrocystic breast changes || 40% || || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | No disease || 30% | + | | No disease || 30% || || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Fibroadenoma || 7% | + | | Fibroadenoma || 7% || Biphasic proliferation of both stromal and epithelial components, arranged into either a pericanalicular pattern (stromal proliferation around epithelial structures), or an intracanalicular pattern (stromal proliferation compressing the epithelial structures into clefts). Fibroadenomas characteristically display hypovascular stroma compared to malignant tumors.<ref name="WHO">{{cite book |editor=Tavassoli, F.A. |editor2=Devilee, P. |title=World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology & Genetics: Tumours of the breast and female genital organs |publisher=IARC Press |location=Lyon |year=2003 |isbn=978-92-832-2412-9 |url=}}{{page needed|date=February 2017}}</ref><ref name="POW">Pathology Outlines Website. [http://pathologyoutlines.com/breast.html#fibroadenoma] Accessed 12 February 2009.</ref><ref name="Rosen">{{cite book |author=Rosen, PP. |title=Rosen's Breast Pathology |isbn=978-0-7817-7137-5 |edition=3rd|year=2009 }}</ref> Furthermore, the epithelial proliferation appears in a single terminal ductal unit and has duct-like spaces surrounded by a fibroblastic stroma. The basement membrane is intact.<ref name="titleFibroadenoma of the breast">{{cite web |url=http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/fibroadenoma-breast-pathology.php |title=Fibroadenoma of the breast |access-date=2007-12-15 }}</ref> |
| + | | [[File:Micrograph of a fibroadenoma.jpg|180px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Other benign mammary dysplasias and neoplasms || 13% | + | | Other benign mammary dysplasias and neoplasms || 13% || || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Breast cancer || 10% | + | | Breast cancer (in situ or invasive) || 10% || See next section. || |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Breast cancer=== | ||
[[File:Pie chart of incidence and prognosis of histopathologic breast cancer types.png|thumb|310px|Breast cancer types, with relative incidences and prognoses.]] | [[File:Pie chart of incidence and prognosis of histopathologic breast cancer types.png|thumb|310px|Breast cancer types, with relative incidences and prognoses.]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Evaluation of tumors}} | {{Evaluation of tumors}} | ||
{{Bottom}} | {{Bottom}} | ||
Revision as of 06:47, 2 October 2019
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
Contents
Gross examination
Selection and trimming
- Determine total specimen size. Optionally, determine weight[1]
- Ink margins.Template:Ink note If sample orientations are marked, use different colors for different directions.[1]
- Palpate specimen for masses. Compare with radiograph if available[1]
- Make 3-4 mm thick slices.[1]
- Submit:[1]
- Entire specimen if it can fit in 3-5 slices.
- If larger, 1 slice per cm of tumor (minimum of 3 slices of tumor), including both center and periphery of tumor.
- Additional suspicious areas, including those indicated by mammography
See also: General notes on gross processing
Report
- Size of original tissue sample, preferably in 3 dimensions.
- Tumor properties, at least:
Microscopic evaluation
If tumor is found, determine:
- Tumor size
- Malignancy
- Distance from excision margin
Malignancy
The most important is to classify a sample as either of the following:
- Benign
- Carcinoma in situ
- Invasive cancer
Most common types
| Finding | Relative incidence |
Histopathology | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrocystic breast changes | 40% | ||
| No disease | 30% | ||
| Fibroadenoma | 7% | Biphasic proliferation of both stromal and epithelial components, arranged into either a pericanalicular pattern (stromal proliferation around epithelial structures), or an intracanalicular pattern (stromal proliferation compressing the epithelial structures into clefts). Fibroadenomas characteristically display hypovascular stroma compared to malignant tumors.[3][4][5] Furthermore, the epithelial proliferation appears in a single terminal ductal unit and has duct-like spaces surrounded by a fibroblastic stroma. The basement membrane is intact.[6] | 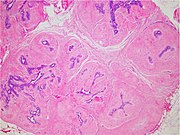
|
| Other benign mammary dysplasias and neoplasms | 13% | ||
| Breast cancer (in situ or invasive) | 10% | See next section. |
Breast cancer
- Further information: Evaluation of tumors
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Monika Roychowdhury. Grossing (histologic sampling) of breast lesions. Pathologyoutlines.com. Topic Completed: 1 August 2012. Revised: 19 September 2019
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson (2007). Robbins Basic Pathology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. p. 739. ISBN 978-1-4160-2973-1.
- ↑ Tavassoli, F.A., ed (2003). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology & Genetics: Tumours of the breast and female genital organs . Lyon: IARC Press. ISBN 978-92-832-2412-9.Template:Page needed
- ↑ Pathology Outlines Website. [1] Accessed 12 February 2009.
- ↑ Rosen, PP. (2009). Rosen's Breast Pathology (3rd ed.). ISBN 978-0-7817-7137-5.
- ↑ . Fibroadenoma of the breast.
Image sources
