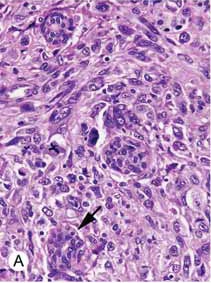
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
Contents
Gross examination
As per:
or mastectomy.
Microscopic evaluation
Differential diagnosis
In invasive ductal carcinoma, malignant cells have penetrated the basement membrane, in contrast to ductal carcinoma in situ.
Staging
Stage by the TNM system as follows in sections below.
Also, look for any angiolymphatic invasion. If present, check whether it reaches outside the tumor, and if so, how far.[1] Give greatest dimension (,or 3 dimensions, generally by adding up the estimated thicknesses of involved slices)).[1]
Primary Tumor (T)Tumor – Depends on the tumor at the primary site of origin, as follows:[2]
Regional Lymph Nodes (N)Lymph Node: The lymph node values depend on the number, size and location of breast cancer cell deposits in various regional lymph nodes, such as the armpit (axillary lymph nodes), the collar area (supraclavicular lymph nodes), and inside the chest (internal mammary lymph nodes.)[3][4] Each stage is as follows:[2]
Critical numbers of involved nodes: 1-3, 4-9, and 10 and over. Note any extranodal extension.[1]
Distant Metastases (M)
Overall stageA combination of T, N and M, as follows:[2]
|
- Further information: Evaluation of tumors
Template:Grading of breast cancer
- Further information: Evaluation of tumors
Report
Breast excision
- Tumor size, if not already given from gross report.[1] Give 3 dimensions or greatest dimension.[1]
- Histopathologic subtype if apparent, but "invasive carcinoma" is acceptable.
- Stage[1]
- Grade, preferably by overall BRE grade. Optionally, give scores for the components thereof.[1]
- Extent of any angiolymphatic invasion.[1]
- Margins of resection,[1] as closest distance from carcinoma to margin in mm or cm or "tumor on ink"/"carcinoma is present on margin". ((If applicable, also specify as "close margins" (no tumor on ink but <2 mm), or "negative margins" (≥2 mm).))[5]
- Results of any immunohistochemistry and other tests[1]
- HER2 as a score or status.
- Ki-67, preferably as labeling index
Example:
| Breast excision with 70 x 55 x 18 mm ductal invasive breast cancer. Nottingham grade II. Estrogen receptor positive, progesterone receptor negative, HER2 receptor score 0, Ki-67 index 17%, T1b. Radically removed. |
Needle or core biopsy
- Histopathologic subtype if apparent, but "invasive carcinoma" is acceptable.
- Results of any immunohistochemistry and other tests, as per excision[1]
- Presence of absence of lymphatic and/or vascular invasion[1]
- Optionally: Provisional grading. Grading can alternatively be deferred to excision.[1]
- State if studies are deferred for a later excision sample[1]
For cancers, generally include a synoptic report, such as per College of American Pathologists (CAP) protocols at cap.org/protocols-and-guidelines.
- synoptic report example
- Tumor type: invasive ductal carcinoma with micropapillary pattern
- Tumor size: greatest microscopic measurement of invasive carcinoma in positive core(s)): 0.7 cm
- In-situ component: no
- Microscopic grading (Nottingham modification of the Bloom-Richardson system):
- Only applies to infiltrating ductal and lobular carcinoma:
- Tubule formation: Little or none (score =3)
- Nuclear pleomorphism: Marked variation in size, nucleoli, chromatin clumping, etc. (score =3)
- Mitotic count : Less than 6 mitoses per 10 hpf (score =1)
- Composite score: 7 points (applies to infiltrating ductal and lobular carcinoma only)
- Histologic grade: Grade II: 6-7 points
- Nuclear grade: grade 3
- Microcalcifications: Present in non-neoplastic tissue
- Lymphocytic host response: absent
- Necrosis: absent
- Blood vessel invasion: absent
- Lymphatic and/or vascular invasion: absent
- Skin involvement: not applicable
- Results of immunohistochemical stains for prognostic markers (as per original report):
- Estrogen Receptor (ER) Status: Positive (greater than 10% of cells demonstrate nuclear positivity)
- Percentage of Cells with Nuclear Positivity: 91-100%
- Average Intensity of Staining: Strong
- Progesterone Receptor (PgR) Status: Positive
- Percentage of Cells with Nuclear Positivity: 51-60%
- Average Intensity of Staining: Strong, moderate and weak
- Estrogen Receptor (ER) Status: Positive (greater than 10% of cells demonstrate nuclear positivity)
- HER-2 by IHC: 2+ / Equivocal
- REFLEX HER-2 FISH TEST: Nonamplificed (ratio 1.5; 3.5 Her-2 signals/cell)
- Ki-67:
- Percentage of Cells with Nuclear Positivity: 43%
- Primary Antibody: MIB1
- Cold Ischemia and Fixation Times: 3 minutes
- Fixation Time (hours): 14 hours and 33 minutes
- Fixative: formalin
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 . Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast (Carcinoma of No Special Type). Stanford Medical School. Retrieved on 2019-10-02.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Originally copied from Fadi M. Alkabban; Troy Ferguson. Cancer, Breast. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Last Update: June 4, 2019. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ↑ "Internal mammary lymphadenopathy in breast carcinoma: CT appraisal of anatomic distribution ". Radiology 167 (1): 89–91. April 1988. doi:. PMID 3347753.
- ↑ "Internal mammary lymphadenopathy: imaging of a vital lymphatic pathway in breast cancer ". Radiographics 10 (5): 857–70. September 1990. doi:. PMID 2217975.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bundred JR, Michael S, Stuart B, Cutress RI, Beckmann K, Holleczek B (2022). "Margin status and survival outcomes after breast cancer conservation surgery: prospectively registered systematic review and meta-analysis. ". BMJ 378: e070346. doi:. PMID 36130770. PMC: 9490551. Archived from the original. .
Image sources