Difference between revisions of "Lobular carcinoma in situ"
m (<noinclude>) |
(→Biomarkers: No) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Top | + | <noinclude>{{Top |
|author1=[[User:Mikael Häggström|Mikael Häggström]] | |author1=[[User:Mikael Häggström|Mikael Häggström]] | ||
|author2= | |author2= | ||
| − | }} | + | }}</noinclude> |
{{Fixation - standard}} | {{Fixation - standard}} | ||
[[File:Histopathology of lobular carcinoma in situ.jpg|thumb|]] | [[File:Histopathology of lobular carcinoma in situ.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Immunohistochemistry for p120 in ductal carcinoma in situ.jpg | Immunohistochemistry for p120 in ductal carcinoma in situ.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | {{Microcalcifications in breast cancer}} | ||
===Biomarkers=== | ===Biomarkers=== | ||
| − | + | Testing for hormone biomarkers is not needed for LCIS (in contrast to [[ductal carcinoma in situ]] where ER/PR is generally indicated). | |
| + | |||
===Microscopic report=== | ===Microscopic report=== | ||
It should contain:<ref>{{cite web|url=https://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/lcis/printable.html|title=Lobular Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast|website=Surgical Pathology Criteria|accessdate=2021-12-14}}</ref> | It should contain:<ref>{{cite web|url=https://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/lcis/printable.html|title=Lobular Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast|website=Surgical Pathology Criteria|accessdate=2021-12-14}}</ref> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
However, grading and staging is not applicable. | However, grading and staging is not applicable. | ||
(Margins of excision are not relevant) | (Margins of excision are not relevant) | ||
| − | + | <noinclude> | |
{{Reporting}} | {{Reporting}} | ||
| − | {{Bottom}} | + | {{Bottom}}</noinclude> |
Latest revision as of 18:42, 22 December 2023
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
Contents
Fixation
Generally 10% neutral buffered formalin.
Presentations
Microscopic evaluation
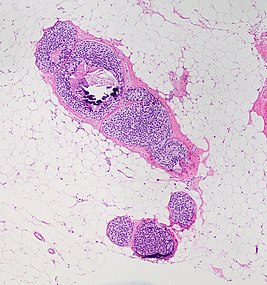
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) typically display monomorphic, loosely cohesive, slightly enlarged and evenly spaced cells that fill acini.[1] Cells have indistinct cell borders, pale cytoplasm, and uniform small nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli.[1]
Differential diagnosis
The main differential diagnosis is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
In DCIS, the cells are cohesive and have high grade atypia.[2]
LCIS typically fills smaller lobules rather than ducts, but DCIS can display lobular cancerization as shown at bottom of image.[image 1]
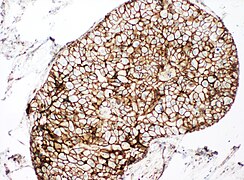
When unsure, perform immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin and p120:
In contrast, both E-cadherin (left image below) and p120 (right) have a membranous staining pattern in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
Microcalcifications

If invasive ductal carcinoma is seen, make at least a low power screening for microcalcifications (to correlate with imaging), but there's no need to look carefully (as tiny microcalcifications would unlikely correlate with imaging anyways).
Biomarkers
Testing for hormone biomarkers is not needed for LCIS (in contrast to ductal carcinoma in situ where ER/PR is generally indicated).
Microscopic report
It should contain:[3]
- Type of resection or biopsy, and location
- Results of any supplementary studies performed
- Extent
However, grading and staging is not applicable. (Margins of excision are not relevant)
See also: General notes on reporting
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sucheta Srivastava. Breast - Noninvasive lobular neoplasia - LCIS classic. Topic Completed: 1 September 2017. Minor changes: 21 June 2020
- ↑ Sucheta Srivastava, M.D.. Breast - Noninvasive lobular neoplasia - LCIS classic (Differential diagnosis section). Topic Completed: 1 September 2017. Minor changes: 17 May 2021
- ↑ . Lobular Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast. Surgical Pathology Criteria. Retrieved on 2021-12-14.
Image sources
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Image(s) by: Mikael Häggström, M.D. Public Domain
- Author info
- Reusing images