Difference between revisions of "Nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

m (Specified) |
(Simplified) Tags: Mobile web edit, Mobile edit |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Look for signs of malignancy. | Look for signs of malignancy. | ||
{{Further|Evaluation of suspected malignancies}} | {{Further|Evaluation of suspected malignancies}} | ||
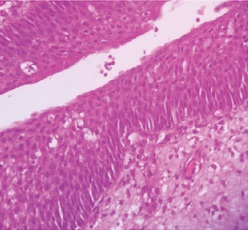
| − | [[File:Histopathology of a nasal polyp.jpg|thumb|'''Benign nasal polyp''' (not otherwise specified), consisting of hyperplastic edematous connective tissue with some seromucous glands and cells representing inflammation (mostly neutrophils and eosinophils) | + | [[File:Histopathology of a nasal polyp.jpg|thumb|'''Benign nasal polyp''' (not otherwise specified), consisting of hyperplastic edematous connective tissue with some seromucous glands and cells representing inflammation (mostly neutrophils and eosinophils), suroounded by respiratory or squamous epithelium.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zm3jBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA168|title=Ear, Nose and Throat Histopathology|last=Michaels|first=Leslie|date=2012-12-06|publisher=Springer Science & Business Media|isbn=9781447133322|language=en|page=168}}</ref>]] |
Main differential diagnoses: | Main differential diagnoses: | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 25 July 2022
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
Nasal polyps
Look for signs of malignancy. Further information: Evaluation of suspected malignancies

Benign nasal polyp (not otherwise specified), consisting of hyperplastic edematous connective tissue with some seromucous glands and cells representing inflammation (mostly neutrophils and eosinophils), suroounded by respiratory or squamous epithelium.[1]
Main differential diagnoses:
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑ Michaels, Leslie (2012-12-06) (in en). Ear, Nose and Throat Histopathology . Springer Science & Business Media. p. 168. ISBN 9781447133322.
Image sources