Skin
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
For skin specimens in general:
Contents
Fixation
Generally 10% neutral buffered formalin.
See also: General notes on fixation
- Suspected immunologic disease:[1] Fixation for immunofluorescence, with for example Michel's solution.[2] For details, see immunofluorescense of skin tissues
Presentations
Most common requests
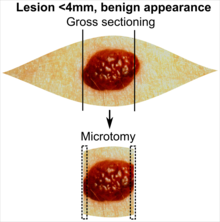
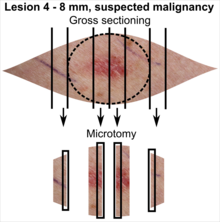
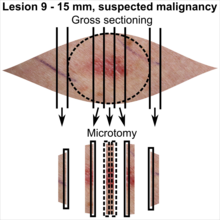
Gross processing of skin excisions
| Lesion size | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| <4 mm | 4 - 8 mm | 9 - 15 mm | |
| Benign appearance | |||
| Suspected malignancy | 
|
|
|
In table above, each top image shows recommended lines for cutting out slices to be submitted for further processing. Bottom image shows which side of the slice that should be put to microtomy. Dashed lines here mean that either side could be used. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions
Microscopic evaluation
If the referral does not point to any particular request (see "Most common requests" above), the following algorithm may be applied:
- Is it a suspected malignant skin excision? If not:
- If primarily inflammatory, evaluate as dermatitis. If none of these, evaluate as:
- Benign non-inflammatory skin conditions, including skin cysts
In intraoperative consultations by frozen section, it is generally sufficient to report clear margins if present, and specification of the type of tumor can be deferred to permanent sections.
Reporting
Preferably see specific articles from algorithm in section above.
- Optionally, the presence of a keratinized squamous epithelium.
- Any abnormalities, generally preceded by location in terms of epidermal, dermal or more specific layers thereof.
- If malignant:
- Degree of differentiation
- Radicality/Least distance to a margin
- Perineural or vascular invasion if present
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
- ↑ The excision examples show a normal mole (upper row, benign appearance) and a superficial basal cell carcinoma (lower row, suspected malignancy).
Main page
References
- ↑ Page 678 in: Chhabra, Seema; Minz, RanjanaWalker; Saikia, Biman (2012). "Immunofluorescence in dermatology ". Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology 78 (6): 677. doi:. ISSN 0378-6323. Archived from the original. .
- ↑ Katarzyna Lundmark, Krynitz, Ismini Vassilaki, Lena Mölne, Annika Ternesten Bratel. Handläggning av hudprover – provtagningsanvisningar, utskärningsprinciper och snittning (Handling of skin samples - Instructions for sampling, cutting and incision. KVAST (Swedish Society of Pathology). Retrieved on 2019-09-09.
- ↑ There are many variants for the processing of skin excisions. These examples use aspects from the following sources:
- . Handläggning av hudprover – provtagningsanvisningar, utskärningsprinciper och snittning (Handling of skin samples - sampling instructions, cutting principles and incision. Swedish Society of Pathology.
- For number of slices and coverage of lesions, depending on size. - Monica Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Måsbäck, Otto Ljungberg. Stora utskärningen. KVAST (Swedish Society of Pathology). Retrieved on 2019-09-26.
- For slices towards the tips to determine radicality, which can be parallel to the slices through the lesions (shown), or as longitudinal slices that go through each tip. - . Dermatopathology Grossing Guidelines. University of California, Los Angeles. Retrieved on 2019-10-23.
- For microtomy of the most central side at the lesion - "The principles of mohs micrographic surgery for cutaneous neoplasia
- With a "standard histologic examination" that, in addition to the lesion, only includes one section from each side along the longest diameter of the specimen.
- It also shows an example of circular coverage, with equal coverage distance in all four directions.
- The entire specimen may be submitted if the risk of malignancy is high. - . Handläggning av hudprover – provtagningsanvisningar, utskärningsprinciper och snittning (Handling of skin samples - sampling instructions, cutting principles and incision. Swedish Society of Pathology.
Image sources