Difference between revisions of "Template:Squamous-cell like skin proliferations - differential diagnosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| [[Actinic keratosis]] || Atypical keratinocytes confined on basal layer. || [[File:Micrograph of actinic keratosis - low magnification.jpg|190px]] | | [[Actinic keratosis]] || Atypical keratinocytes confined on basal layer. || [[File:Micrograph of actinic keratosis - low magnification.jpg|190px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Keratoacanthoma || Symmetrical and circumscribed proliferation of keratinocytes, with central horn plug, with epidermis that extends over the tumor. Highly differentiated SCC. | + | | Keratoacanthoma || Symmetrical and circumscribed proliferation of keratinocytes, with central horn plug, with epidermis that extends over the tumor. Highly differentiated SCC. || [[File:Keratoacanthoma (2197016163).jpg|190px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Adnexal carcinomas || Squamous differentiation, but does not show connection with the epidermis and highlights adnexal features. || [[File:Micrograph of microcystic adnexal carcinoma - superficial follicular keratin-filled cysts.jpg|190px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Adenosquamous carcinoma || Mixed glandular and squamous differentiation. || [[File:Micrograph of cutaneous adenosquamous carcinoma - 40x.jpg|190px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma<ref group="notes> | |
| − | + | *''Buschke–Löwenstein tumor'' is an alternative name for verrucous squamous cell carcinoma in the ano-genital region. | |
| − | | Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma<ref group="notes> | + | *''Carcinoma cuniculatum'' is a characteristic form of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma on the sole. |
| − | | | + | </ref> || Exophytic squamous proliferation with marked papillomatosis and low atypia and the presence of koilocyte-like changes. Found in head and neck locations, as well as in the genitalia and sole of the foot. ||rowspan=2| [[File:Micrograph of penile verrucous carcinoma - 20x.jpg|190px]]<br> [[File:Micrograph of penile verrucous carcinoma - 200x.jpg|190px]] |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Inverted follicular keratosis || Sharply circumscribed endophytic verrucous proliferation with prominent squamous features. | | Inverted follicular keratosis || Sharply circumscribed endophytic verrucous proliferation with prominent squamous features. | ||
Revision as of 07:28, 28 October 2019
Author:
Mikael Häggström [note 1]
Contents
Squamous cell-like proliferations: Differential diagnosis
| Condition[1] | Characteristics[1] | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Invasive squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin | Atypical and pleomorphic keratinocytes, involving the dermis and the sub-cutis with a potential metastatic spread. | 
|
| Squamous-cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen’s disease) | Atypical keratinocytes at every layer of epidermis. | 
|
| Actinic keratosis | Atypical keratinocytes confined on basal layer. | 
|
| Keratoacanthoma | Symmetrical and circumscribed proliferation of keratinocytes, with central horn plug, with epidermis that extends over the tumor. Highly differentiated SCC. | 
|
| Adnexal carcinomas | Squamous differentiation, but does not show connection with the epidermis and highlights adnexal features. | 
|
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | Mixed glandular and squamous differentiation. | 
|
| Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma[notes 1] | Exophytic squamous proliferation with marked papillomatosis and low atypia and the presence of koilocyte-like changes. Found in head and neck locations, as well as in the genitalia and sole of the foot. | 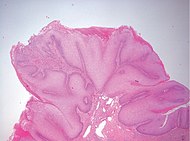 
|
| Inverted follicular keratosis | Sharply circumscribed endophytic verrucous proliferation with prominent squamous features. | |
| Seborrheic keratosis | Acanthosis, absence of atypia, pseudo-horn cysts, in inflamed lesions, mitoses may be present. | |
| Bowenoid papulosis | Atypical keratinocytes and mitoses. Histology similar to Bowen’s disease. | |
| Metastasis | Personal medical history of the patient, nodular proliferation without connection to epidermis, immunohistochemical evaluation. |
Notes
- ↑
- Buschke–Löwenstein tumor is an alternative name for verrucous squamous cell carcinoma in the ano-genital region.
- Carcinoma cuniculatum is a characteristic form of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma on the sole.
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details.
Main page
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Initially copied from: Paolino, Giovanni; Donati, Michele; Didona, Dario; Mercuri, Santo; Cantisani, Carmen (2017). "Histology of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: An Update ". Biomedicines 5 (4): 71. doi:. ISSN 2227-9059. - "This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)."
Image sources